JavaScript Array Mastery: 25 Top Methods to Streamline Your Code
25 Essential Array Methods for Effortless Coding!
Table of contents
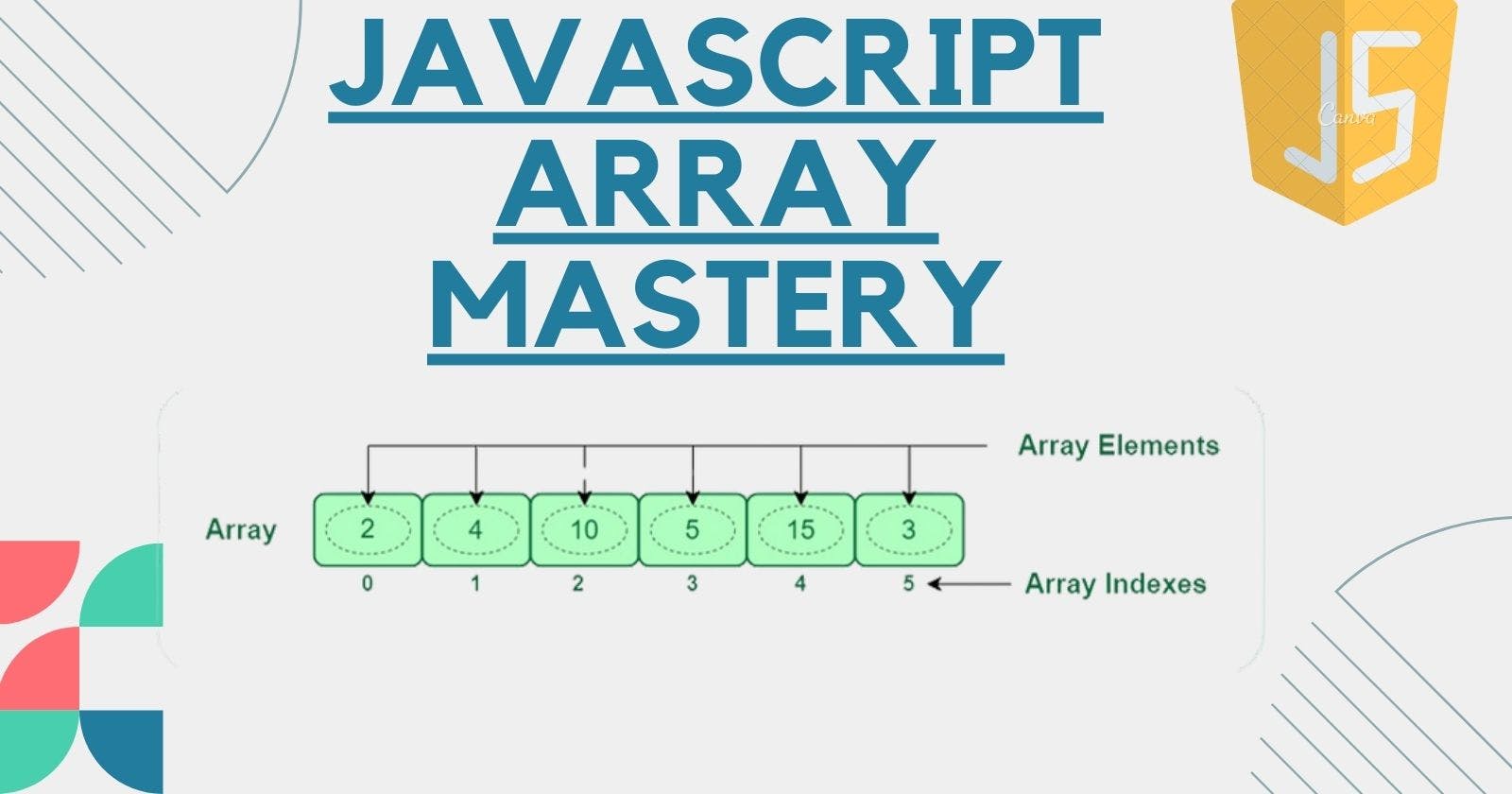
Javascript array is a data structure used to store multiple data types such as string , numbers , bigInt , boolean , objects and even another array in a single variable which can help in condense and organize your code . Javascript array is a dynamic , meaning it can grow and shrink its size as needed.
There are two ways to create an array in javascript :-
The array literals , using square brackets [ ].
The array constructors , using new keyword.
Javascript array do not have name/value pairs , instead they are indexed with interger value beginning with 0 and can be accessed by referring the index number of the item in square bracket.
Javascript array is mutable , meaning you can modify their elements after they are created .They offer various methods for iteration , manipulation and transformation of their items. Array methods are build-in features of the javacsript that we can apply to our array , that saves us from writing common function from scratch .
Javascript Methods.
1. Array.map()
This method create a new array by applying function to the each element of the array , this method doesn't modify the existing array. But instead it returns a new array as results of applying function to every element of existing array .
const arr = [101 , 201 , 301 , 401 , 501]
const newArray = arr.map((everyElement) =>{
return everyElement+= 4;
})
console.log(newArray)
// [ 105, 205, 305, 405, 505 ]
2. Array.forEach()
This method execute a provided function once to each element of the array without creating a new array.
const colors = ["red" , "blue" , "green" , "black" , "white"]
colors.forEach((color , index)=>{
console.log(`color at index : ${index} :- ${color}`)
})
// color at index : 0 :- red
// color at index : 1 :- blue
// color at index : 2 :- green
// color at index : 3 :- black
// color at index : 4 :- white
3. Array.every()
This method is used to checks every element in an array passed the certain condition specified by the callback function . It returns ' true ' if all the elements satisfy the condition otherwise return false .
const arr = ["nikhil" , "opensourse" , "mern" ]
const isString = arr.every((element) =>{
return typeof element === 'string'
})
console.log(isString)
// true
4. Array.some()
This method is used to check at least one element in an array satisfies the certain condition specified in the callback function . It returns 'true' if atleast one element satisfy the condition otherwise it returns 'false' .
const arr = ["nikhil" , "opensourse" , "mern" , 2001 ]
const isNumber = arr.some((element) =>{
return typeof element === 'number';
})
console.log(isNumber)
// true
5. Array.includes()
This method is used to check if an array contains a specific element . It returns 'true' if the array contains the element otherwise it returns 'false'.
const niks = ["HTML" , "CSS" , "Javascript" , "NodeJS" , "MongoDB"]
console.log(niks.includes("CSS")) // True
console.log(niks.includes("Typescript")) // False
6. Array.find()
This method is used to retrieve the value of the first element in an array that satisfies the provided condition .
let arr = [45 , 55 , 65 , 75 , 85]
let foundNumber = arr.find((number)=>{
return number > 70;
})
console.log(foundNumber) //75
7.Array.findIndex()
This methods return the index of the first element in an array that pass the test in a testing function.
let arr = ["sun" , "moon" , "stars" , "nikhil"]
let index = arr.findIndex((element)=>{
return element === "nikhil"
})
console.log(index) //3
8.Array.indexOf()
This method is used to find the index of the specified item in an array, It returns the first index at which the element is found in the array or '-1' if it is not present.
let arr = [101 , 202 , 303 , 404 , 505]
console.log(arr.indexOf(404)) //3
9.Array.concat()
This method is used to merge two or more arrays and returns a new array.It does not change the existing array.
let arr1 = [101 , 202 , 303 , 404 , 505]
let arr2 = ["Nikhil" , "opensource" , "WebDeveloper"]
let arr3 = ["Hashnode" , "Nikhil's Blog"]
console.log(arr1.concat(arr2).concat(arr3))
[ 101, 202, 303, 404, 505, 'Nikhil', 'opensource','WebDeveloper','Hashnode',
"Nikhil's Blog" ]
10.Array.join()
This method is used to join the all elements of an array into single string separated by specified operator and returns the resulting string.
let fruits = ["apple" , "orange" , "grapes"]
let result = fruits.join(' , ')
console.log(result) //apple , orange , grapes
11.Array.filter()
This method is used to create a new array with all the element which passes the condition specified in a callback function.
let arr1 = [101 , 202 , 303 , 404 , 505]
let evenArr = arr1.filter((number) => {
return number%2 == 0
})
console.log(evenArr) // [ 202, 404 ]
12. Array.reduce()
This method is used to accumulate or combine elements of an array into a single value. It iterates over each element of an array , applying the callback function and accumulate or combine into single value.
let arr = [101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105]
let sum = arr.reduce((total , currentValue)=> total + currentValue)
console.log(sum) //515
13 . Array.fill()
This method is used to fill the array with the static value , starting from the specified index and ending from another specified index.
let arr = new Array(5)
console.log(arr) // [empty,empty,empty,empty,empty]
console.log(arr.fill(25,0,5)) // [ 25, 25, 25, 25, 25 ]
14.Array.slice()
This method is used to extract a section of the array with specified start to end elements and return a new array with the extracted elements.
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
let slicedArr = arr.slice(3,8)
console.log(slicedArr) // [ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ]
15.Array.splice()
This method is used to change the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing element and/or adding new elements in place.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
let removedElement = arr.splice(1 , 1 , "GSOC")
console.log(arr) //[ 'MERN', 'GSOC', 'Development', 'DevOps' ]
console.log(removedElement) // [ 'Opensource' ]
16.Array.reverse()
This method is used to reverse the order of elements in an array.It modifies the original array in place and return the new array.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
let reversedArr = arr.reverse()
console.log(reversedArr) // [ 'DevOps', 'Development', 'Opensource', 'MERN' ]
17.Array.push()
This method is used to adds one or more elements at the end of the array and returns the new length of the array.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
console.log(arr.push("GSOC")) // 5
console.log(arr) // [ 'MERN', 'Opensource', 'Development', 'DevOps', 'GSOC' ]
18.Array.pop()
This method is used to remove the last element from the end of the array and returns the removed elements.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
console.log(arr.pop()) // DevOps
console.log(arr) // [ 'MERN', 'Opensource', 'Development' ]
19.Array.unshift()
This method is used to adds one and more elements to the starting of an array and returns the length of the array.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
console.log(arr.unshift("GSOC" , "AI/ML")) // 6
console.log(arr)
// [ 'GSOC', 'AI/ML', 'MERN', 'Opensource', 'Development', 'DevOps' ]
20. Array.shift()
This method is used to remove the first element from the starting of the array and returns the removed element.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
console.log(arr.shift()) //MERN
console.log(arr) // [ 'Opensource', 'Development', 'DevOps' ]
21.Array.sort()
This method is used to sort the elements of an array in place and then returns the sorted array .The default sort order is ascending order , built upon the element into strings , then comparing the sequences of UTF-16 code unit values.
When applied to an array of string , it sorts the elements alphabetically but for numeric sort , a compare function is required.
// Ascending Order (By Default)
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
let sortedArr = arr.sort()
console.log(sortedArr)
// [ 'DevOps', 'Development', 'MERN', 'Opensource' ]
// Decending Order
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
let sortedArr = arr.sort((a , b) => b.localeCompare(a))
console.log(sortedArr)
// [ 'Opensource', 'MERN', 'DevOps', 'Development' ]
let arr = [101, 506, 456, 234, 353, 244];
let ascOrder = arr.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let descOrder = arr.sort((a, b) => b - a);
console.log(ascOrder); // [ 101, 234, 244, 353, 456, 506 ]
console.log(descOrder); // [ 506, 456, 353, 244, 234, 101 ]
22.Array.toString()
This method is used to convert an array into a string . it returns a string representing the array elements separated by commas.
let arr = ["MERN" , "Opensource" , "Development" , "DevOps"]
let stringRepresentation = arr.toString()
console.log(stringRepresentation) // MERN,Opensource,Development,DevOps
23.Array.isArray()
This method is used to determine whether a given number is a array or not. It returns true if the value is an array , otherwise , it returns false.
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let notArr = "HelloWorld"
console.log(Array.isArray(arr)) //true
console.log(Array.isArray(notArr)) //false
24.Array.toLocaleString()
This method is used to return the string representing the elements of an array. Each element is converted to a string using the toLocaleString Function , which typically uses locale-specific formatting options( such as date , time , and number formatting ) defined for the user's environment.
let priceArr = [12, 34.89, 765.34, 101, 99.99];
console.log(
priceArr.toLocaleString('en-US', {
style: 'currency',
currency: 'INR'
})
);
// ₹12.00,₹34.89,₹765.34,₹101.00,₹99.99
let arr = [new Date('07 Mar 2024 17:44:06 UTC')]
const localeString = arr.toLocaleString('en', { timeZone: 'UTC' });
console.log(localeString) // 3/7/2024, 5:44:06 PM
25.Array.from()
This method is used to create a new , shallow-copied array instance from array-like or iterable object .
let obj = {
length : 5 ,
0 : "Javascript",
1 : "Java" ,
2 : "Golang" ,
3 : "Python" ,
4 : "C++"
}
let newArr = Array.from(obj)
console.log(newArr)
// [ 'Javascript', 'Java', 'Golang', 'Python', 'C++' ]
Thank You for Reading, Stay tuned for more empowering content! We hope you found valuable insights and inspiration in our blog. Keep exploring, keep learning, and stay curious.
Happy coding! 🚀✨